BED RAIL ENTRAPMENT PREVENTION

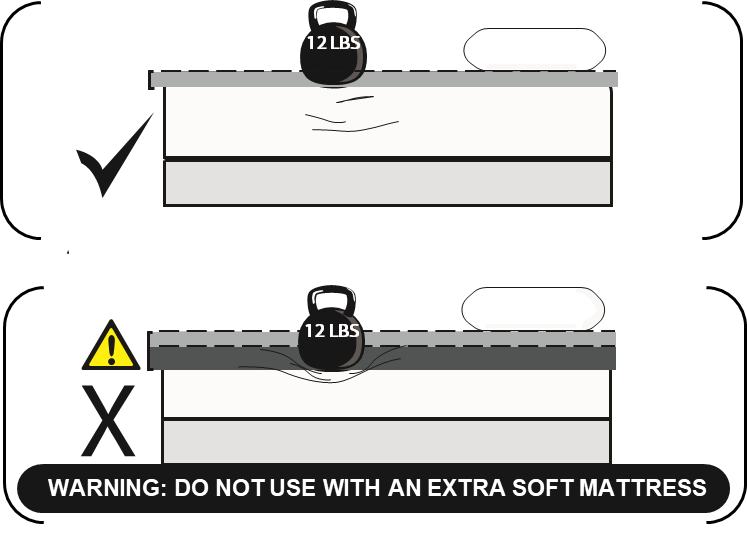
THERE IS A MUCH GREATER RISK OF ENTRAPMENT AND INJURY/DEATH WHEN USING BED RAILS WITH A SOFT MATTRESS! A soft mattress increases the risk that a person’s head, arm, or leg could become entrapped between the mattress and a rail. Entrapment can cause injury or death.
To ensure it is safe to use a bed rail with your mattress, test your mattress by taking your fist and applying about 12lbs (5.4kg) of weight on the edge of the mattress. If the mattress is soft enough that you can compress the mattress by about 2 inches (51cm) when applying 12 lbs (5.4 kg) of weight, do not use a bed rail without the bed rail safety guard. If you have any questions, please call 800-506-9901.


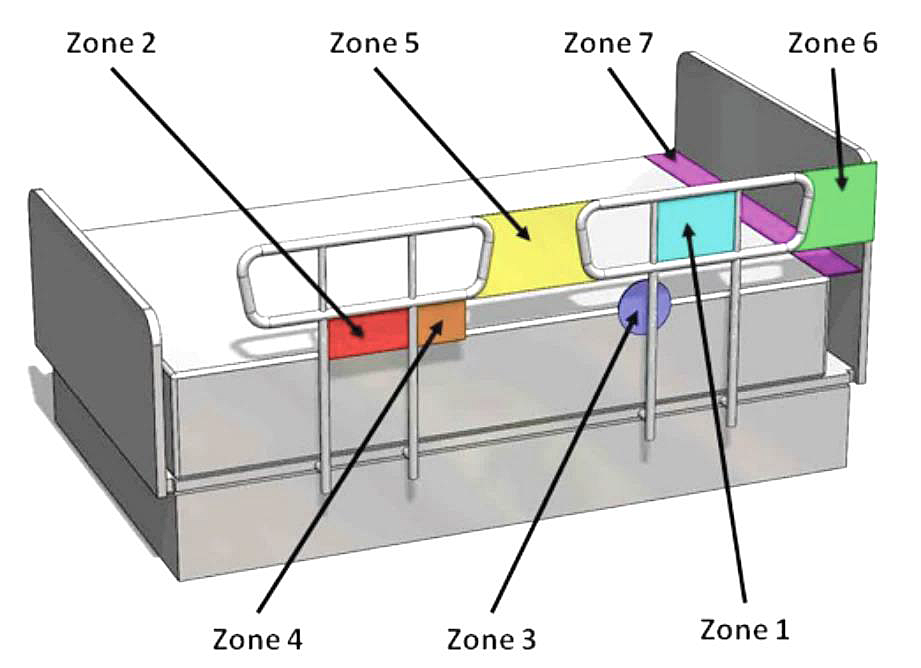
Zone 1: Within the Rail – Any open space between the perimeters of the rail can present a risk of head entrapment. The FDA recommended space is less than 4.75 inches (12 cm).
Zone 2: Under the Rail – The gap under the rail between the mattress, may allow for dangerous head entrapment. The FDA recommended space is less than 4.75 inches (12 cm).
Zone 3: Between the Rail and the Mattress – This area is the space between the inside surface of the bed rail and the mattress, and if too big it can cause a risk of head entrapment. The FDA recommended space is less than 4.75 inches (12 cm).
Zone 4: Under the Rail at the Ends of the Rail – A gap between the mattress and the lowermost portion of the rail poses a risk of neck entrapment. The FDA recommended space is less than 2.375 inches (6 cm). Also, install the bed rail such that the angle at the end of the bed rail relative to the top of a mattress is greater than 60 degrees.
Zone 5: Between Split Bed Rails – When partial length head and split rails are used on the same side of the bed, the space between the rails may present a risk of head, neck, or chest entrapment.
Zone 6: Between the End of the Rail and the Side Edge of the Head or Foot Board – A gap of less than 12.5 inches (32 cm) between the end of the bed rail and the side edge of the headboard or footboard can present the risk of entrapment of the head, neck, or chest.
Zone 7: Between the Head or Foot Board and the End of the Mattress – When there is too large of a space between the inside surface of the headboard and the end of the mattress, the risk of head entrapment increases.